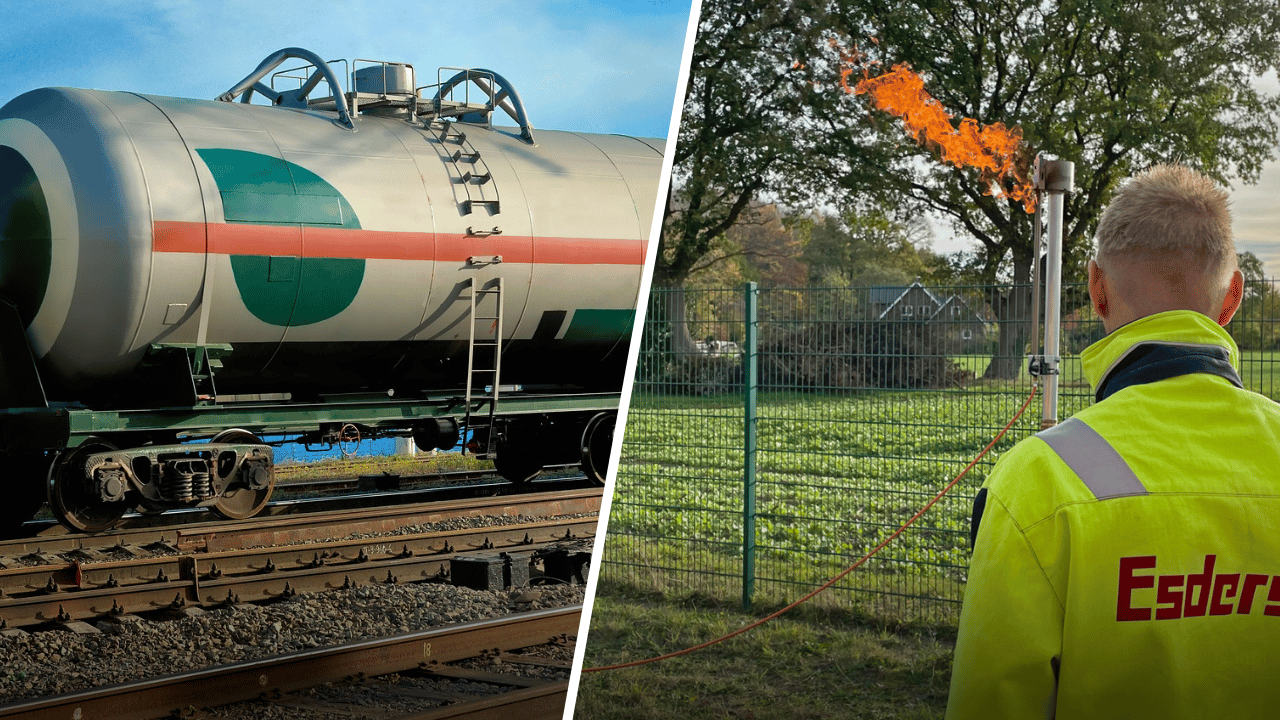
Maintenance, emptying or inerting a Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) tank is an essential process to ensure safe and efficient handling and maintenance. Nowadays, owners are switching to other energy sources more frequently, or the system needs to be serviced, repaired or replaced. To do this, the remaining gas must be removed from the system and the tank inertised. Specialist companies carry out this work safely and efficiently. In this article, we will explore in detail how to carry out this procedure properly.
Table of Contents
What is tank inerting and why is it important?
Inerting is a process prior to decommissioning an LPG tank that consists of removing any flammable or hazardous gas residues from a tank. The aim of inertisation is to reduce the atmosphere inside containers with hazardous, reactive or sensitive substances to below the explosion limits in order to prevent explosions or undesirable chemical reactions. It is essential, especially in the case of LPG tanks, where the presence of propane or butane can pose a considerable risk.
Decommissioning or disposal of a disused Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) tank is essential for safety, regulatory compliance and environmental protection reasons. These tanks can pose potential hazards if not handled correctly, including leaks, explosions or environmental contamination.
Inertisation involves the use of inert gases such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, which displace or isolate the gases present so that contact between oxygen or moisture and reactive materials is prevented. This process is used in various areas such as reactors, tank farms and in the processing of food or pharmaceutical products to ensure product quality and occupational safety. Inertisation is an important component of many safety concepts.
Complying with regulations that require the proper disposal of end-of-life tanks not only helps avoid legal risks and fines, but also demonstrates a commitment to safety, public health and environmental responsibility. In addition, by decommissioning or cancelling these tanks, resources are optimised by freeing up space and reducing maintenance costs, thus contributing to more efficient asset management. For more information, please have a look at the national rules and regulations, for UK it is Liquid Gas UK, Code of Practice 17, for Spain it is the Complementary Technical Instruction MI-IP06 and for Germany DVFG-TRF 2021 – Technische Regel Flüssiggas.
Inertisation of an LPG tank by flaring residual gas
During a gas tank disposal procedure, a gas flare may be used to burn off the residual gases present in the LPG tank in a controlled manner. The main purpose of this process is to reduce the concentration of flammable gases to safe levels, eliminating any explosion or fire hazards associated with the presence of residual gas inside the tank. Moreover, it is an environmentally friendly method, as no harmful gases are released into the atmosphere.
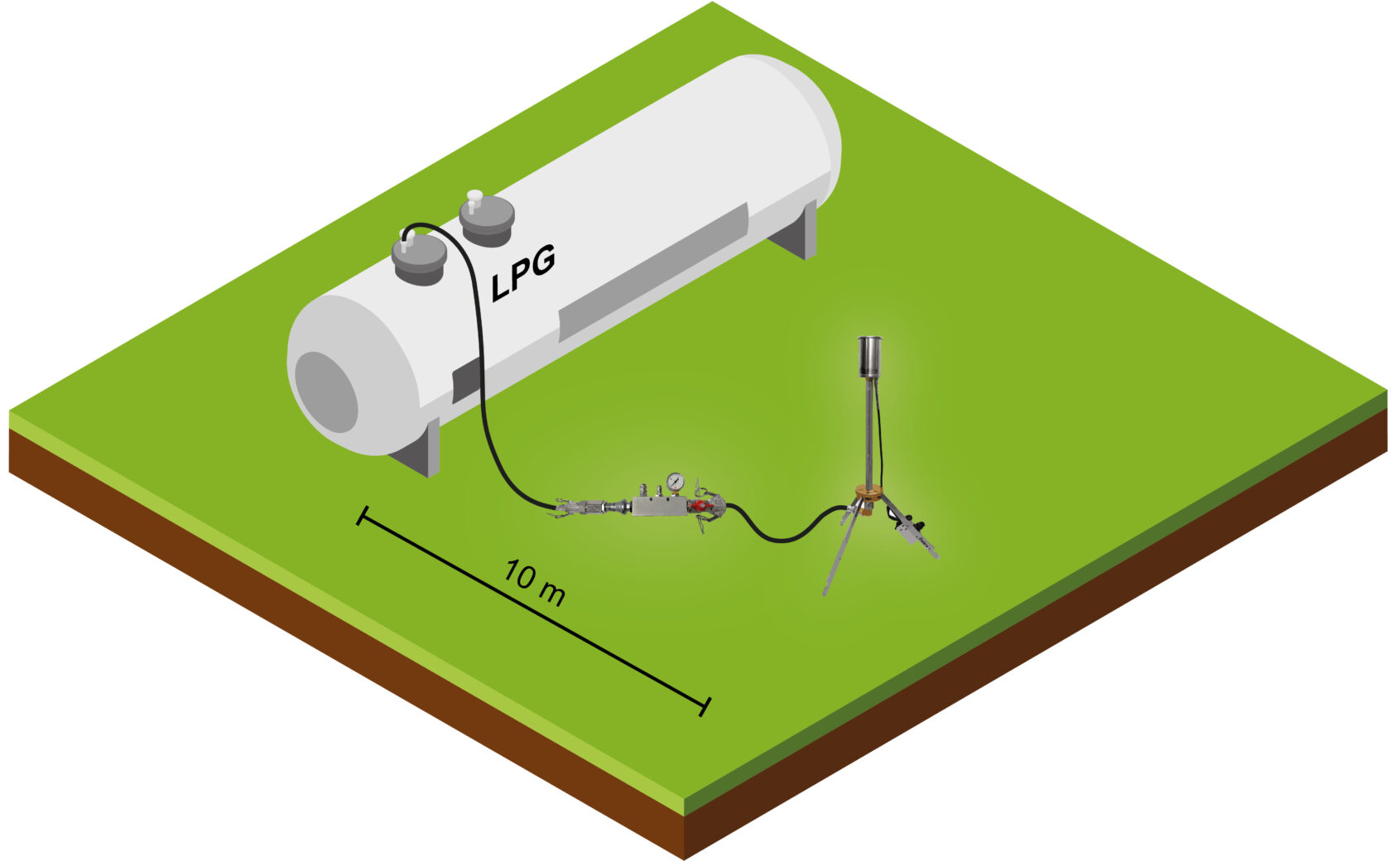
Inerting by flaring waste gases is a fundamental practice to ensure safety and regulatory compliance in the handling of decommissioned LPG tanks. By disposing of residual gases in a controlled manner, the risk of accidents is minimised and people, assets and the environment are protected.
Interested in our portable gas flares? Request a quotation now!
Steps for emptying an LPG tank by controlled flaring
In the following we will list the general steps to be carried out to empty and dispose of a gas tank, in this case an LPG tank.
Preparing a specialised equipment
It is crucial to have a suitable vacuum pump to evacuate the LPG tank safely. In addition, special accessories, such as adapters, must be used to mount the system safely and efficiently.
On the other hand, tank emptying may only be carried out in areas specially designated for this purpose, as required by applicable regulations. It is important to identify and use these authorised areas to comply with legal requirements and to ensure safety during the process.
Pressure check
It is essential to check both the operating pressure of the tank and the maximum inlet pressure of the gas flare to be used during the process. Ensuring that both pressures match is key to avoiding any risk of damage or accident.
Selecting the right flare for the gas tank
Dependent on the volume and pressure of the tank, a specific gas flare may be required to ensure effective inertisation. In some cases, the standard flare may be insufficient, so it is important to select the correct size and type of gas flare.

Controlled residual gas combustion
Once all equipment is prepared and pressures are verified, the inertisation process can proceed. Using gas flares, propane or butane residues are removed from the tank, ensuring a safe and risk-free environment.
Follow-up and safety measures
Cleaning & gas concentration check: After the pressure has dropped to a normal level due to flaring, the gas concentration must be checked with a gas detector. If the concentration is still not safe, the tank must be cleaned by inertisation.
Introducing the inert gas: Nitrogen is the most commonly used gas for inertisation as it is inert and does not support an explosive atmosphere. The nitrogen is introduced into the tank until the atmosphere in the tank is reduced to a safe level.
Monitoring the oxygen level: The oxygen concentration in the tank is constantly monitored to ensure that it remains at a safe level.
Maintenance and inspection: Regular maintenance and inspections of the tank are necessary to ensure that no leaks or other problems affect inertisation.
Advantages of using a portable flare for LPG tank disposal
Gas flares offer several significant advantages during the inerting process of an LPG tank. These advantages include:
Efficiency: The gas flares are highly efficient in removing flammable residues, guaranteeing complete inerting of the tank.
Environmentally friendly: This technology provides an effective and safe solution for the disposal of waste gases, thus protecting both people and the natural environment around us.
Safety: By disposing of waste in a controlled and effective manner, the risk of accidents or explosions during the tank handling process is reduced.
Adaptability: With a wide range of sizes and types available, it is possible to select the right gas flare for each specific application, ensuring optimum results every time.
Sign up for our newsletter now and never miss any updates on rules and regulations!

