Table of Contents
Diffusion through membranes
The gas storage membranes used in biogas plants are made of plastic. However, these are not 100% gas-tight, as a small amount of gas always diffuses through the membrane.
Diffusion through gas storage foils
The diffusion rate depends on:
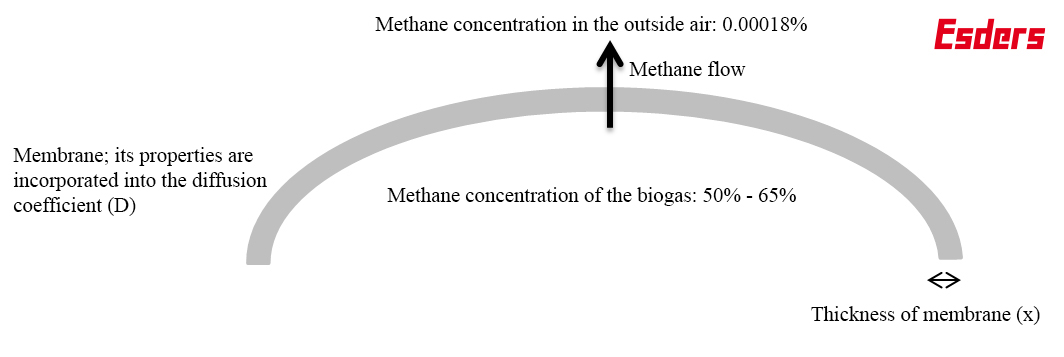
- the concentration gradient of the gas on the inside and outside, i.e. the methane concentration in the tank and in the air. Biogas usually contains between 50 and 65% CH4. The concentration in the outside air is very low and is about 1.8 ppm (or 0.00018 Vol%).
- the material properties of the membrane: the thicker and denser the membrane, the lower the diffusion through the foil
- the degree of stretching of the membrane: the more stretched the membrane is, the thinner it is and it may also lose its gas-tightness when it resumes its original state.
- temperature: the warmer it is, the higher the diffusion through the membrane.
The diffusivity of a gas storage foil can be calculated using ‘Fick’s law of diffusion’. The material properties, temperature and strain (foil thickness) are then incorporated into the calculation of the diffusion coefficient (Picture 1).
Inspection of air domes
An air-supported roof usually consists of two foils (gas membrane and weatherproof foil) stretched over the digester. A fan blows air between the two foils, building up pressure and stretching the weatherproof foil upwards. The gas membrane is pushed up by the pressure in the gas chamber and pushed down by the pressure between the gas membranes. This results in the gas membrane bulging, depending on the operating state of the biogas plant (gas level), in order to store biogas (Picture 2).
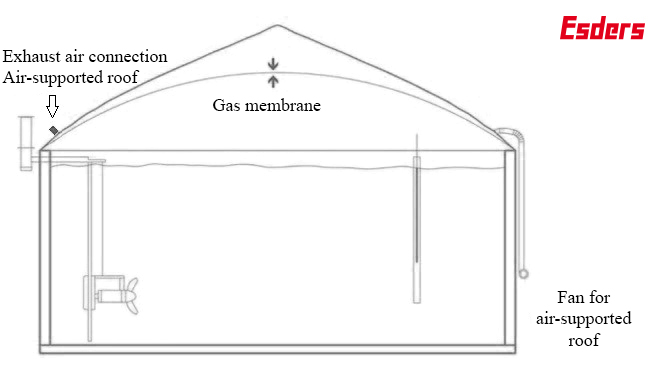
Since the fan for the air-supported roof continuously blows air between the gas foils and air continuously escapes at the exhaust air connection (ideally on the opposite side of the container), the space between the gas membrane and the weather protection foil is permanently ventilated. A certain methane permeability cannot be avoided (see introduction), so that a low methane concentration can be measured at the exhaust air connection even during normal operation.
The space between the gas membrane and its outer casing is to be monitored in accordance with chapter 3.5 of TRAS 120 to detect leaks in the gas membrane:
‘A supporting air monitoring system must be installed on the side opposite the air inlet. The exhaust air flow of the intermediate space must be monitored for biogas leaks. The measured values must be read daily and evaluated weekly, unless this is done automatically. The values must be documented. If the plant is subject to the Major Accidents Ordinance, monitoring must be continuous, with the values being recorded.’
The reason for this requirement is that, although a certain methane concentration is to be expected due to diffusion, a concentration that is too high indicates a leak in the gas membrane.
The following describes how to check the permissible diffusion of methane through the membrane on site.
Procedure in practice
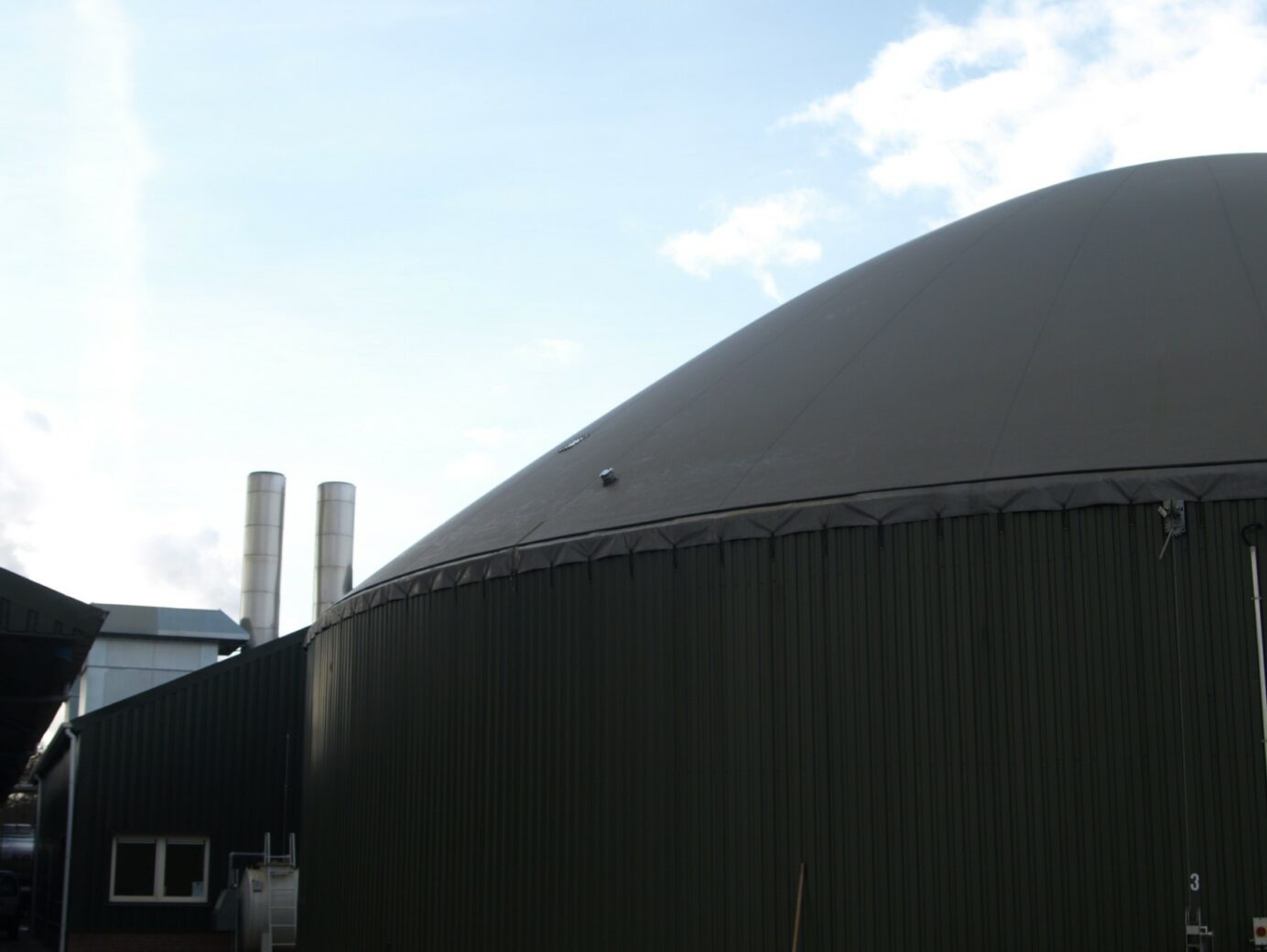

Before the actual measurement begins, the position of the exhaust air socket or sockets must be determined.
Monitoring the methane concentration of the supporting air flow
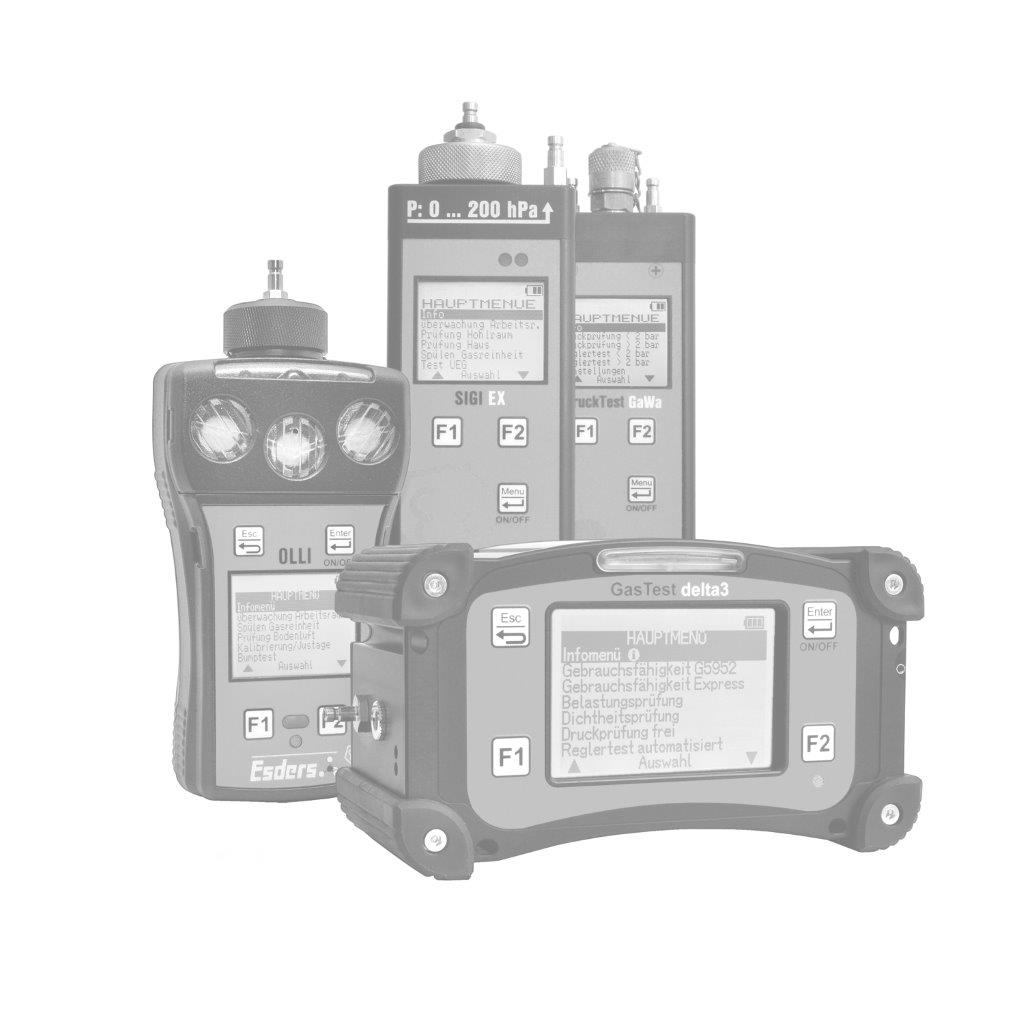
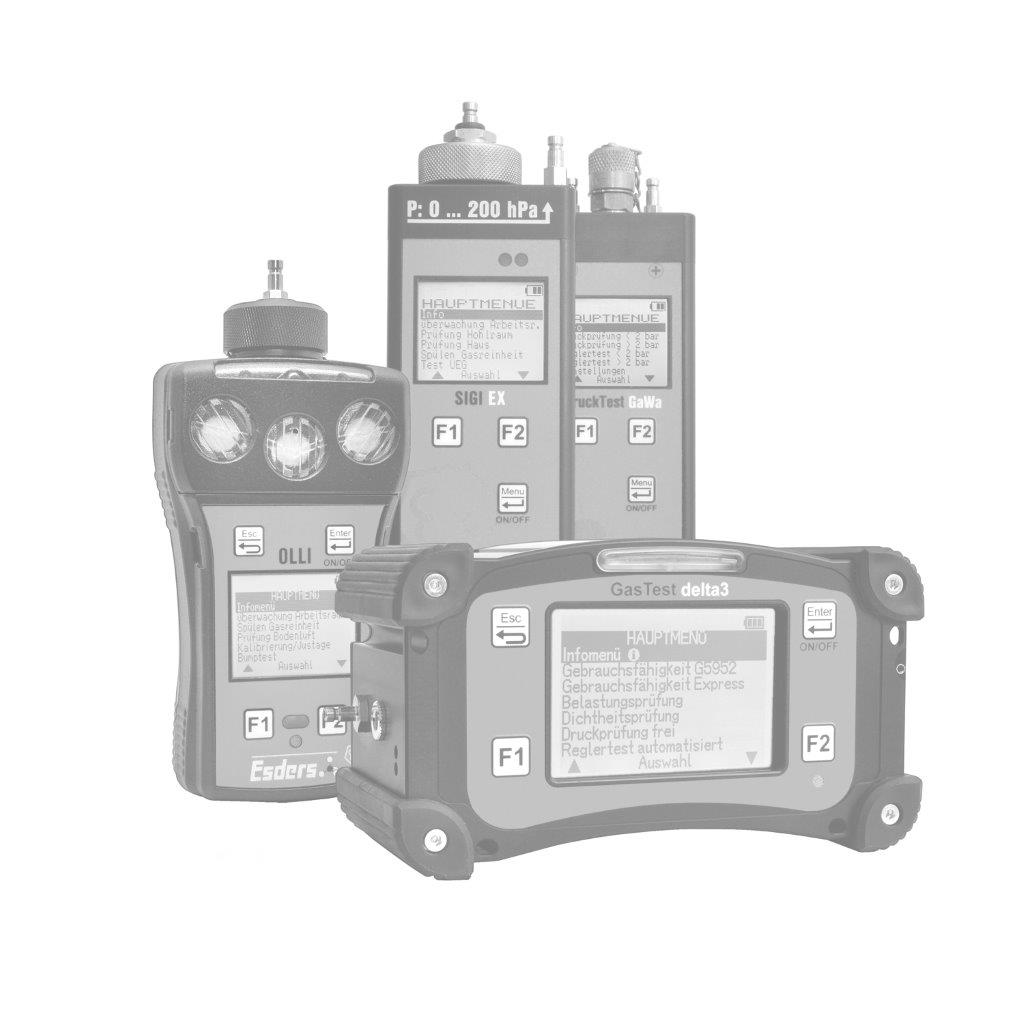
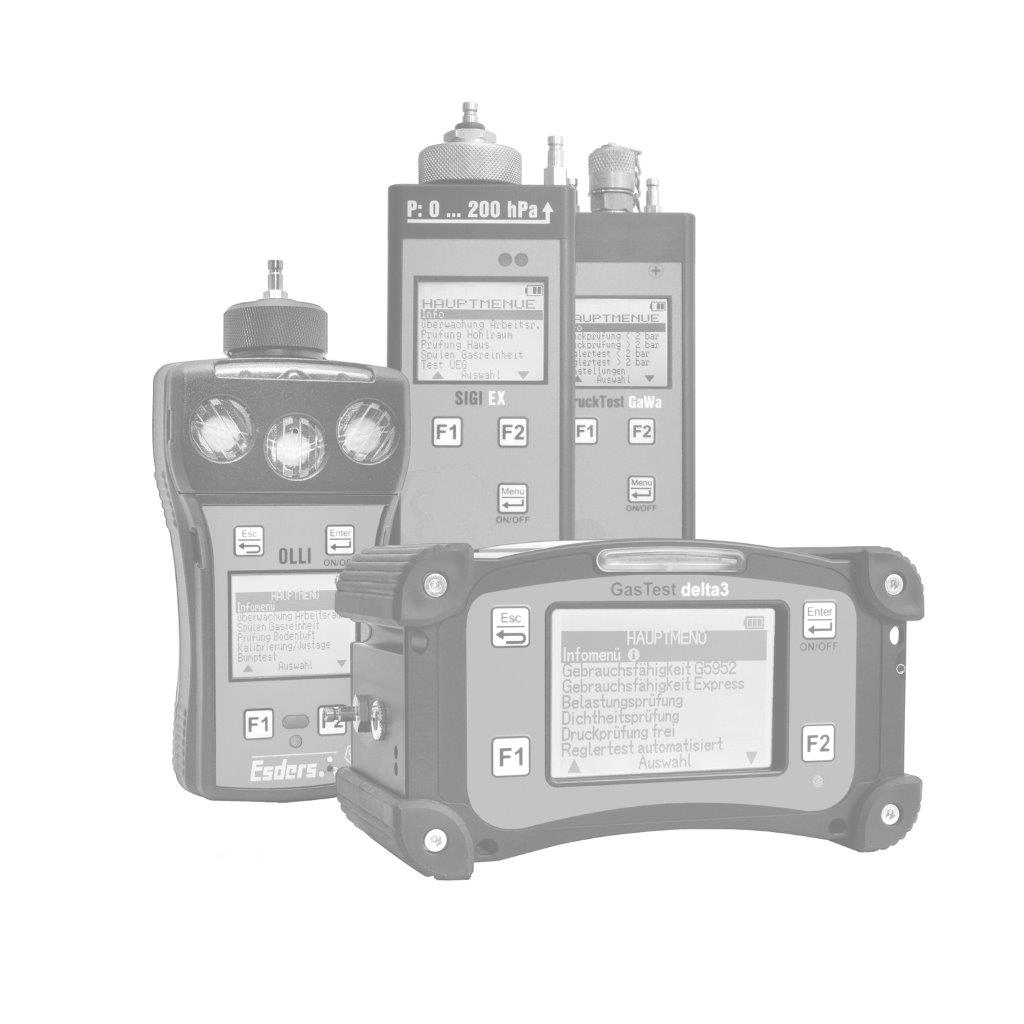
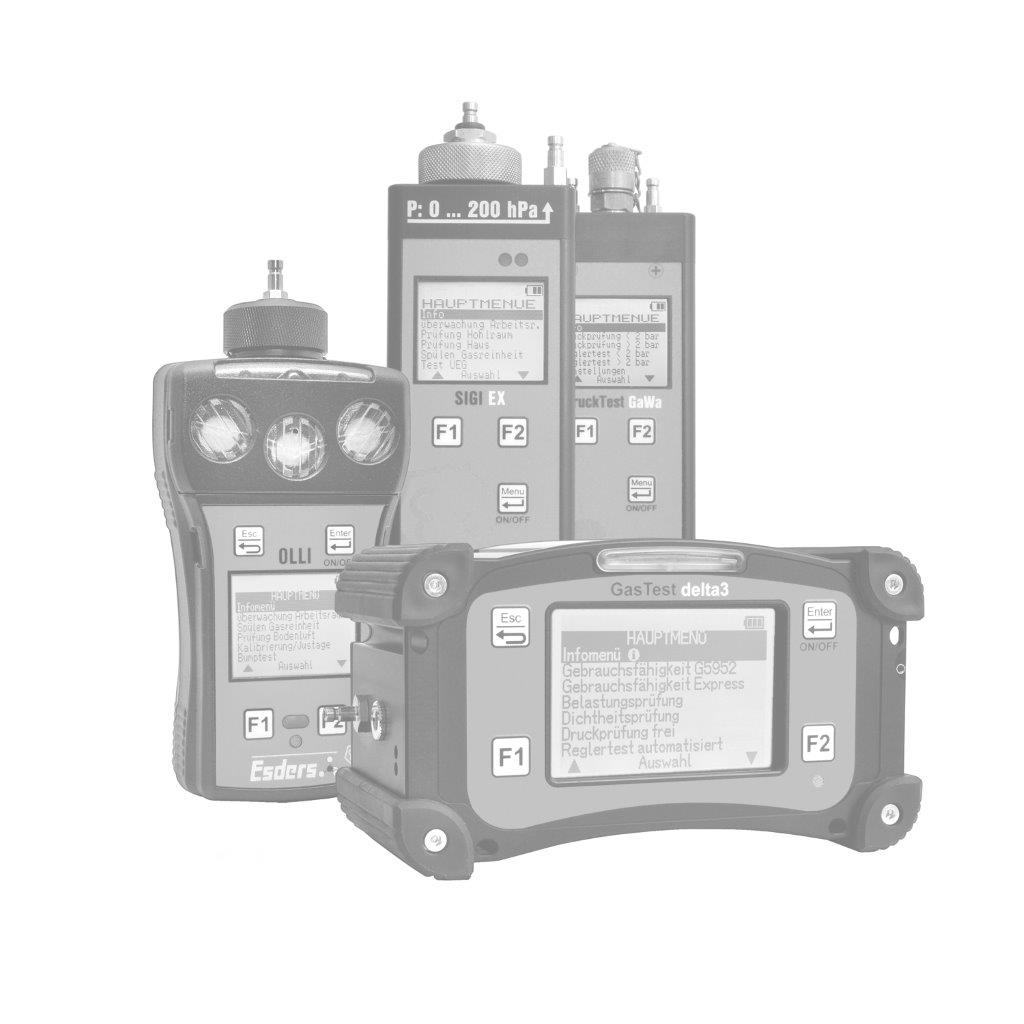
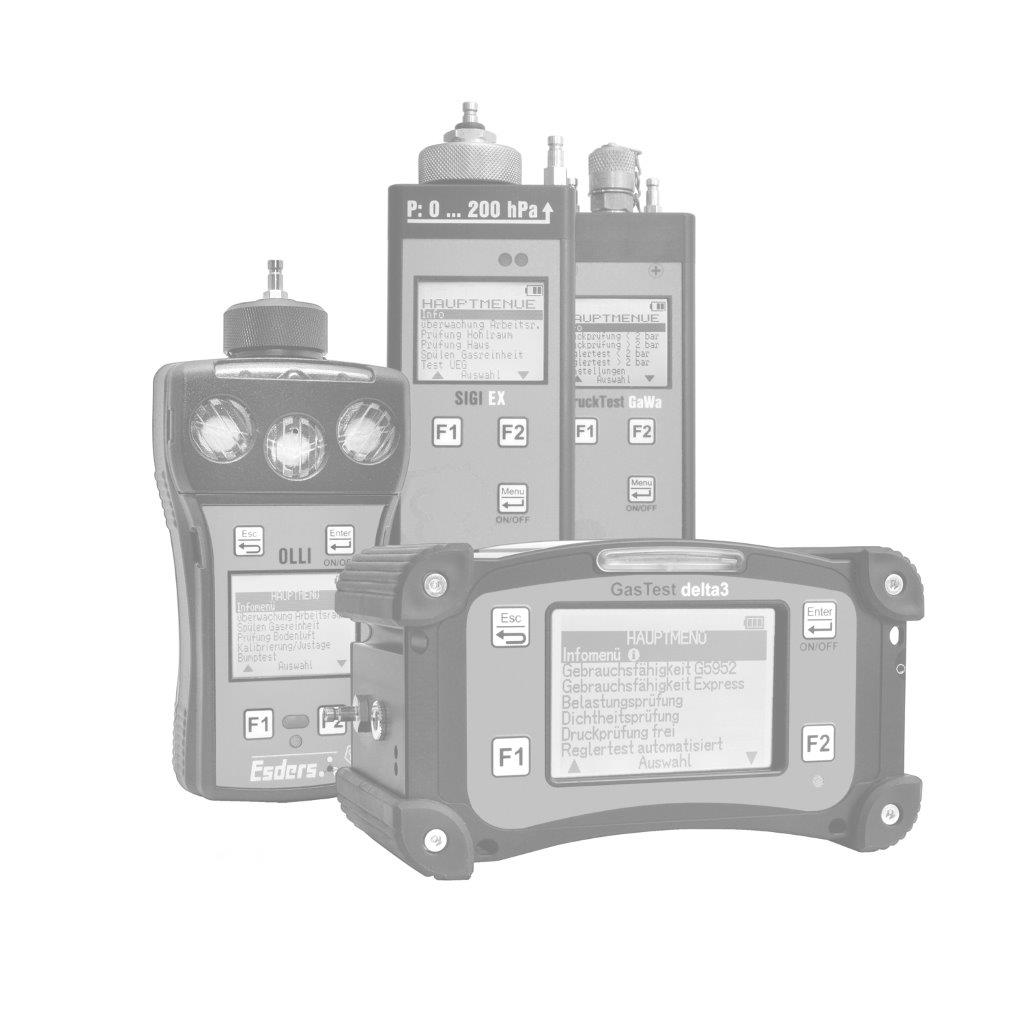
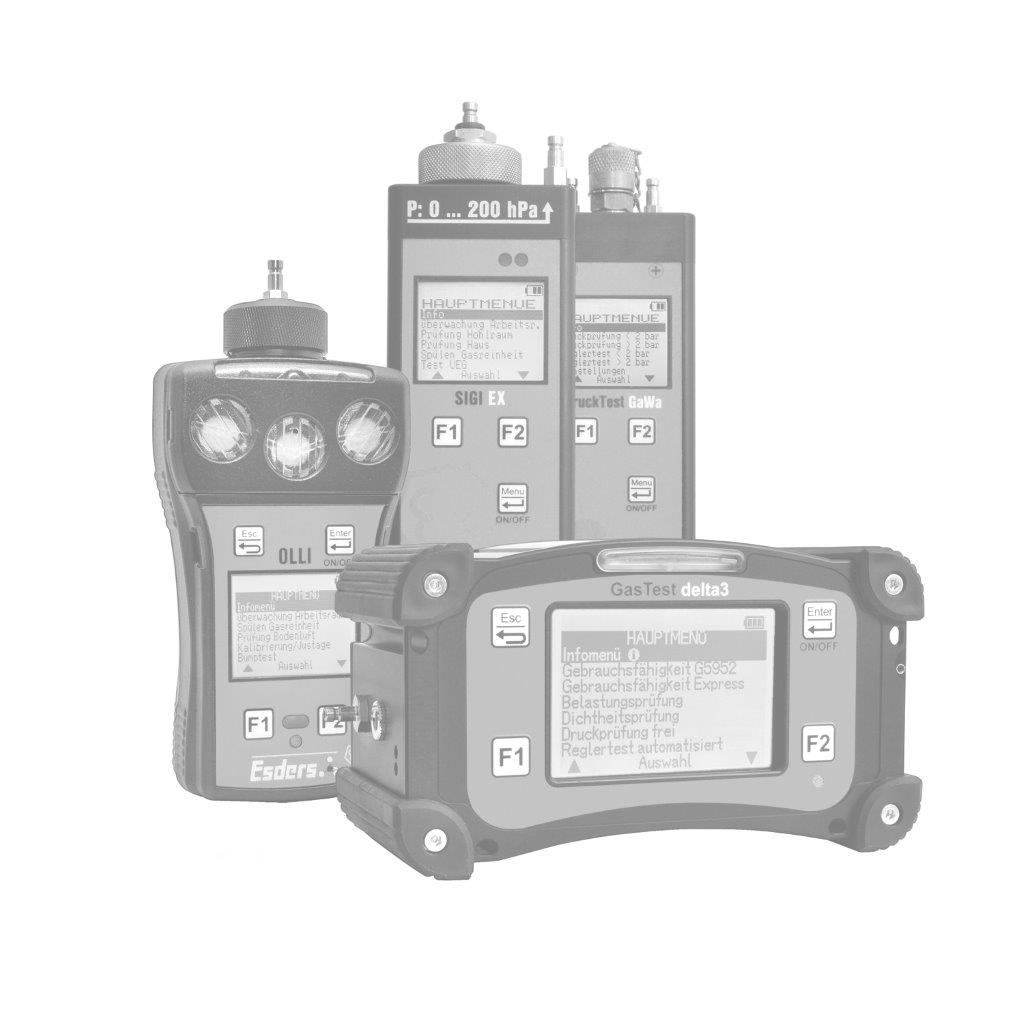
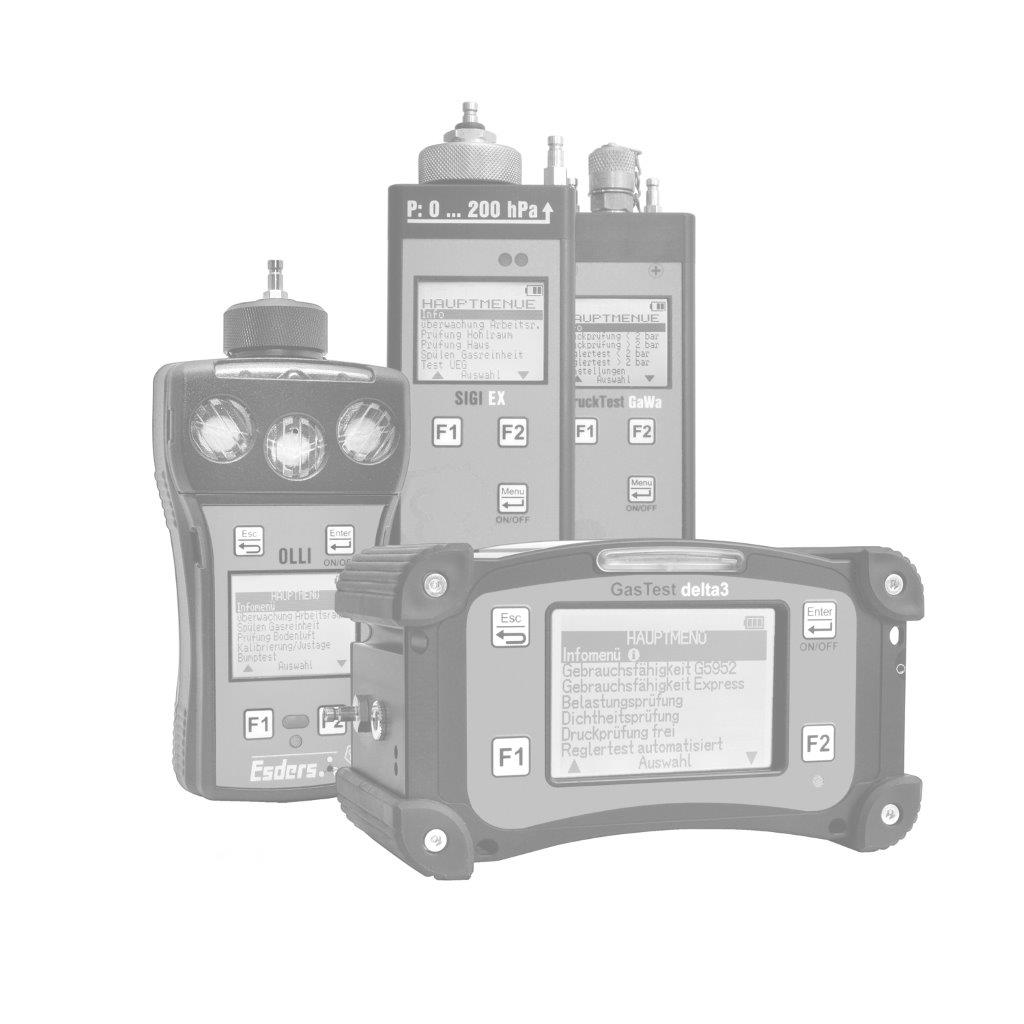
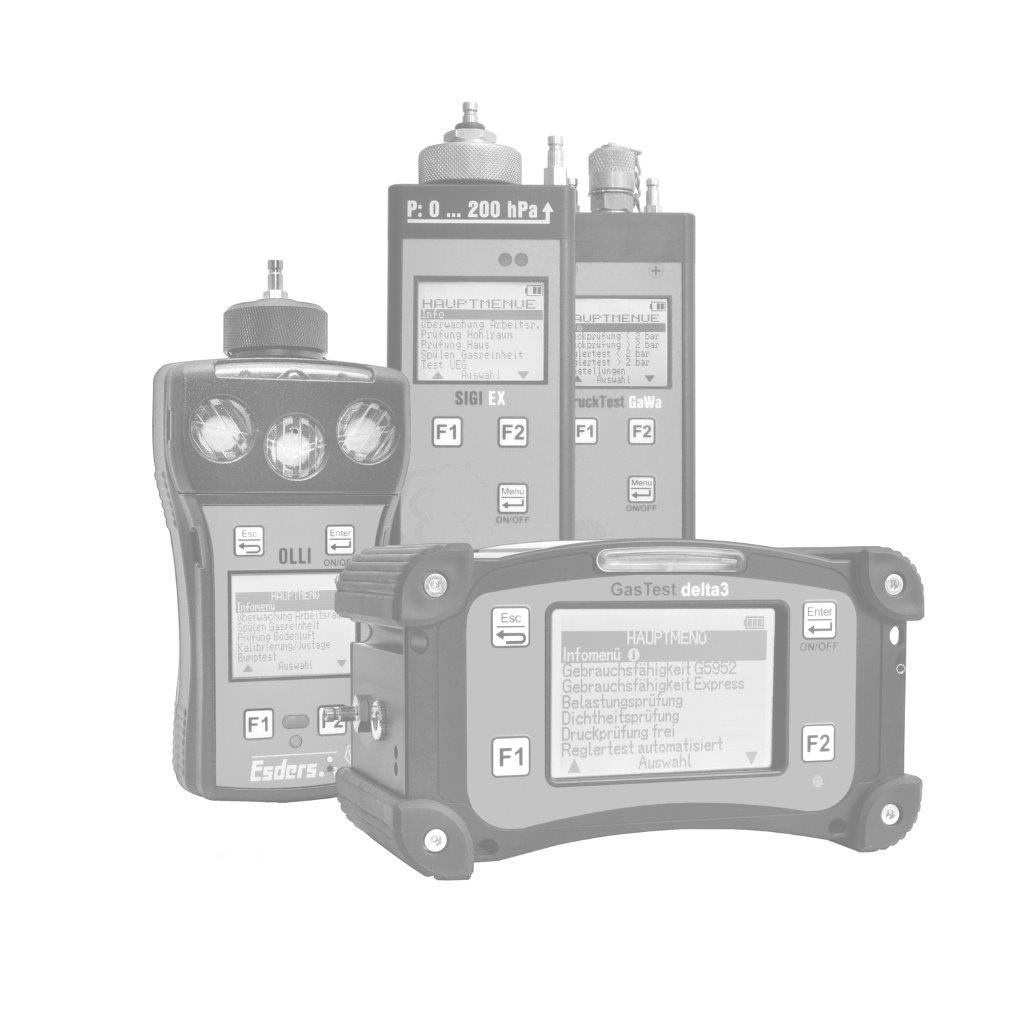
The gas concentration in the supporting air flow is determined using a gas detector. It is important that the concentrations are measured in the ppm (parts per million) range. This can be done, for example, with our gas detector OLLI in the Building Inspection menu.
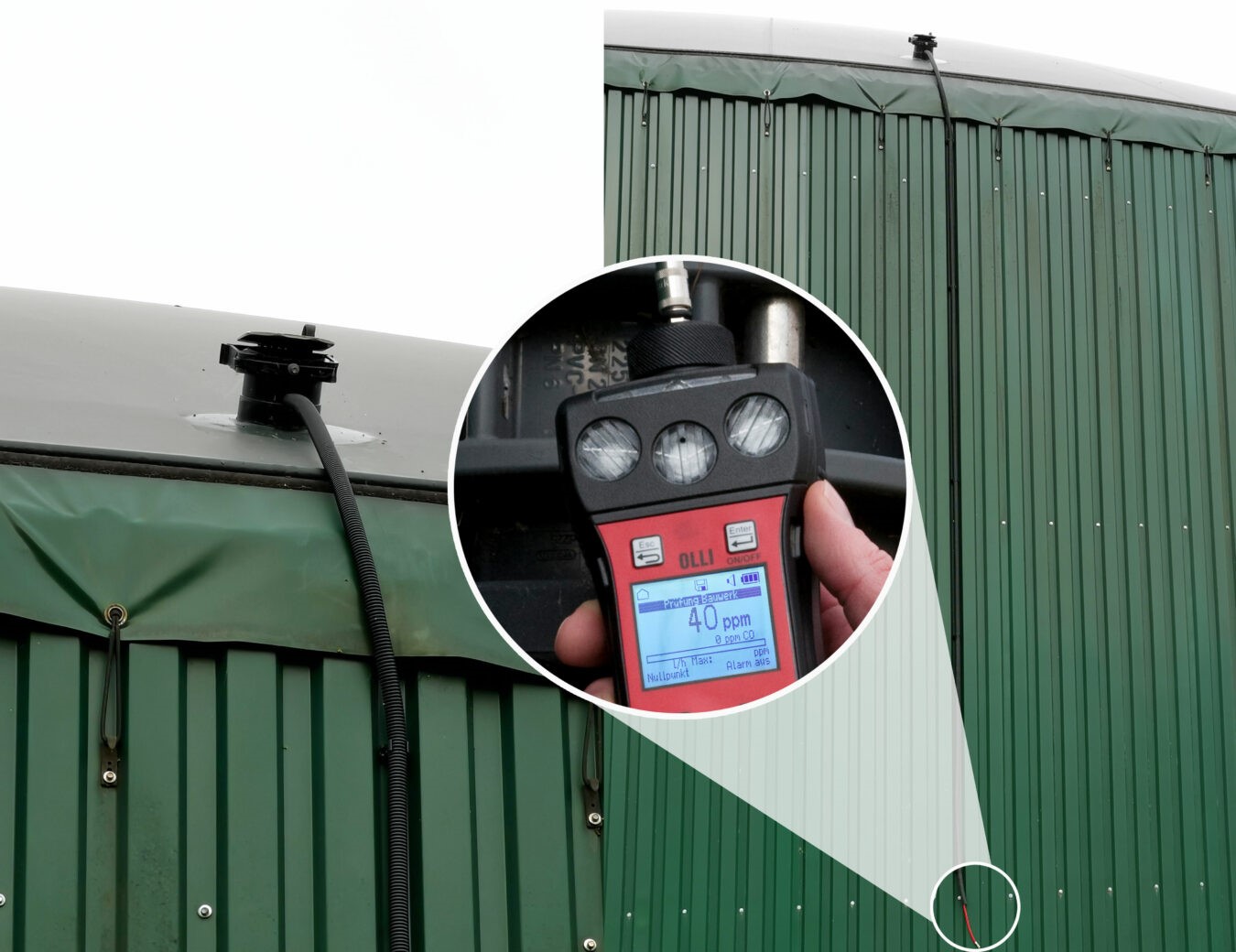

The measurement can be taken either directly at the exhaust air connection. Alternatively, as shown in the picture, a hose connection can be installed from the blower outlet along the edge of the container. This allows the gas concentration in the supporting air flow to be measured comfortably without ladders, etc.
The OLLI is an explosion-proof, compact diffusion hand-held measuring device for up to five combustible and toxic gases as well as oxygen in an extremely durable 2K plastic enclosure with a rechargeable and explosion-proof Li-ion battery pack. It can be fitted with up to three gas sensors (Ex/Ox/Tox). The device can optionally be equipped with a pump and pressure measurement function. It is configured individually according to customer requirements.
To perform the measurement, the menu item ‘Building inspection’ is used in the OLLI, which reacts particularly sensitively in the lower measuring range at very low concentrations (ppm range). It is important to let the sensor run in in fresh air before starting the measurement so that the zero point is set correctly.

How do I calculate the permissible methane concentration?
To calculate the permissible methane concentration, the following parameters are required:
- surface area of the gas foil (in m²)
- air volume flow at the exhaust nozzle (in m³/h)
The volume flow at the exhaust air hood is measured once with an anemometer.
The area of the gas foil can be calculated, for example, simply using a spherical segment. Only the diameter of the container and the height of the gas foil are used as parameters here. The formula for this spherical segment is:
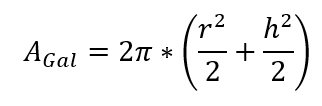
AGal: surface area of the gas foil (spherical cap) m²
r: radius of container [m]
h: height of gas foil above edge of container [m]
The maximum methane concentration due to diffusion is then calculated using the following formula:
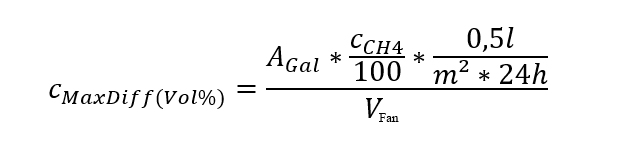
To simplify the calculation, we have created software based on these formulas, into which only the measured gas concentration and the constants of the biogas plant have to be entered. In addition to evaluating whether the gas foil is tight, the resulting methane losses are also calculated.
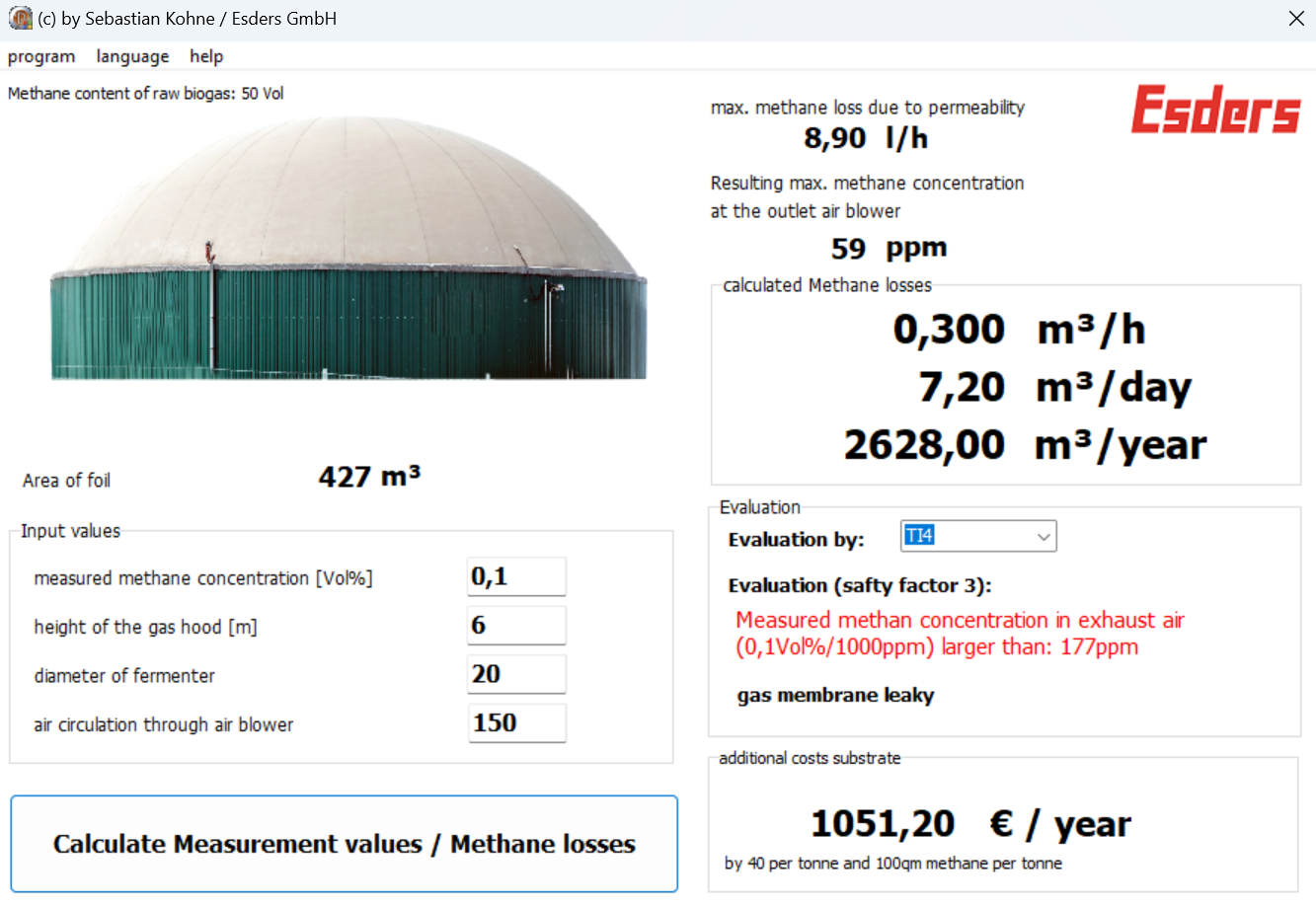
Do you want to use our software to calculate the methane losses from your biogas plant? Then simply fill out the form. You will receive an e-mail from us with a link to the download. The software is free of charge for you.
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)
.jpg?width=100)